In situ Vaccination Followed by Intramuscular poly-ICLC Injections for the Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Mouse Models - ScienceDirect

Cancers | Free Full-Text | Intratumoral (Poly-ICLC) Therapy for Dogs with Advanced Cancers: First Report on Clinical Effectiveness, Quality of Life, and Adverse Events
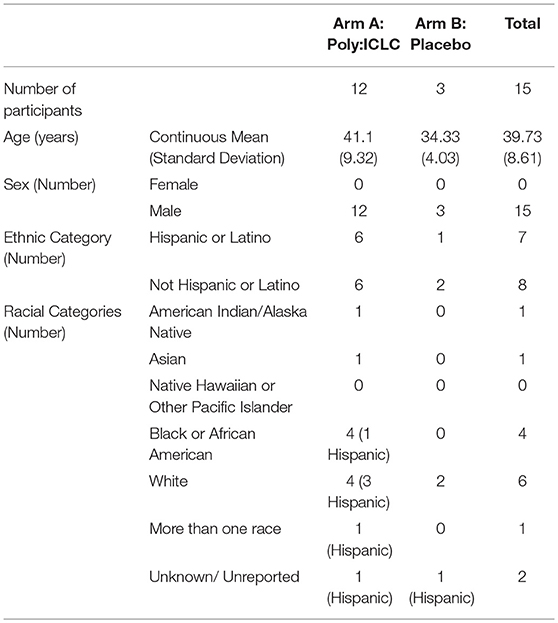
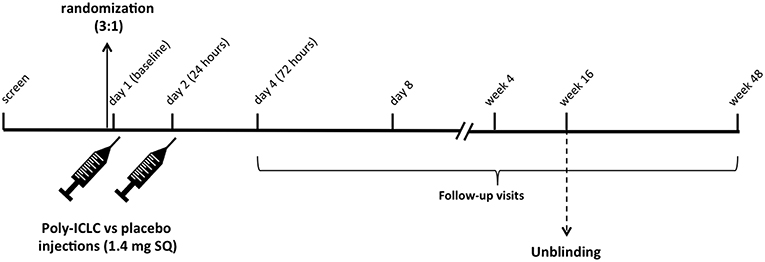
Frontiers | Poly-ICLC, a TLR3 Agonist, Induces Transient Innate Immune Responses in Patients With Treated HIV-Infection: A Randomized Double-Blinded Placebo Controlled Trial
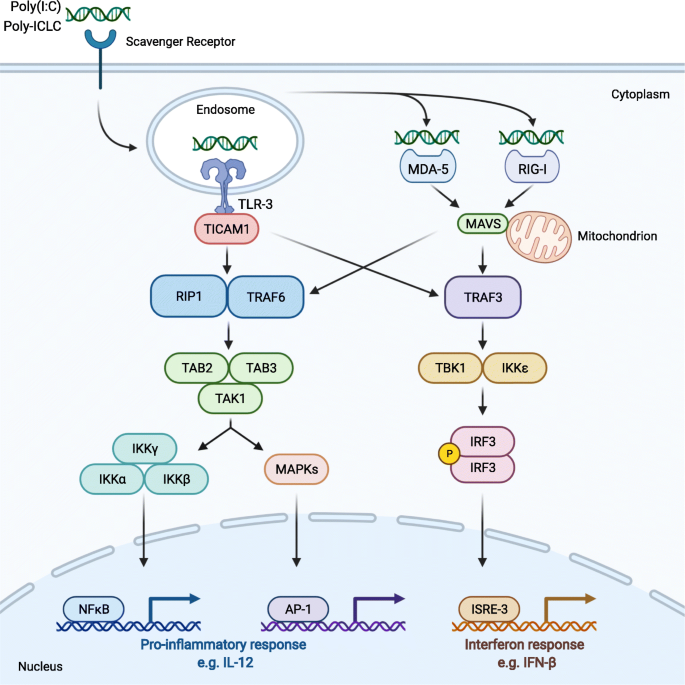
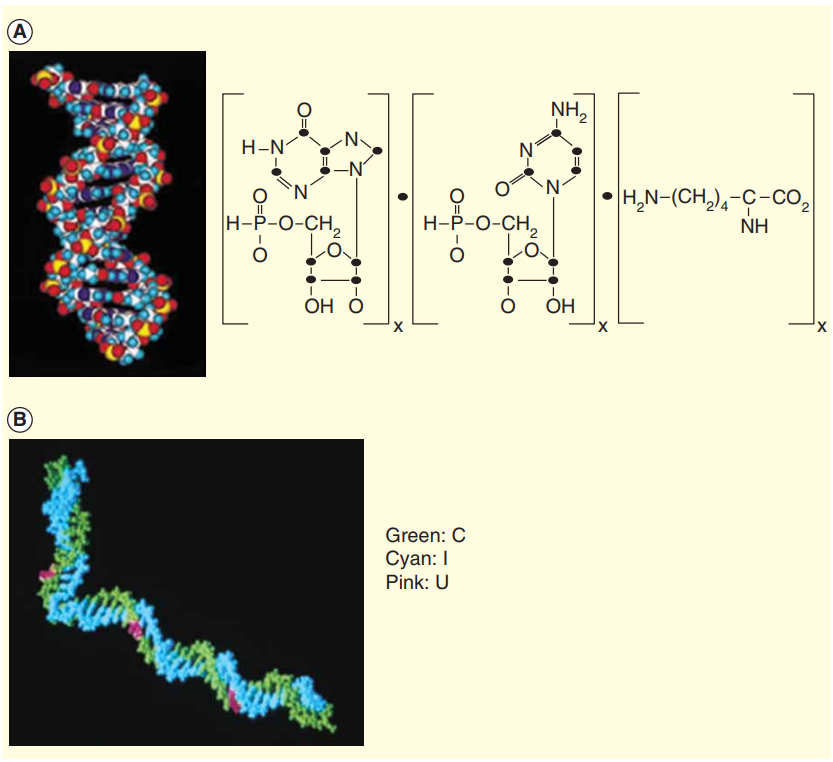
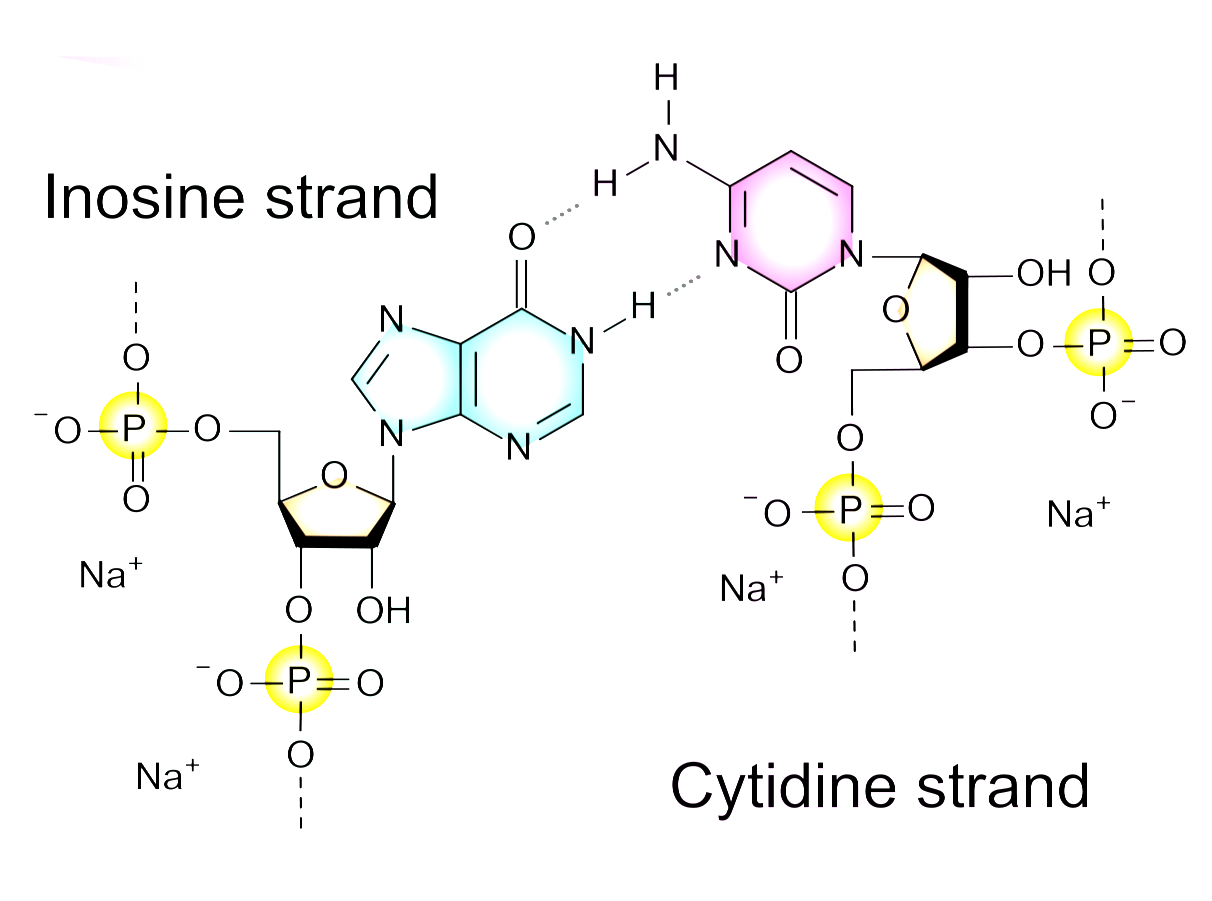
A systematic review on poly(I:C) and poly-ICLC in glioblastoma: adjuvants coordinating the unlocking of immunotherapy | Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research | Full Text

Cytosolic Receptor Melanoma Differentiation–Associated Protein 5 Mediates Preconditioning-Induced Neuroprotection Against Cerebral Ischemic Injury | Stroke

Poly‐ICLC preconditioning protects the blood–brain barrier against ischemic injury in vitro through type I interferon signaling - Gesuete - 2012 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library
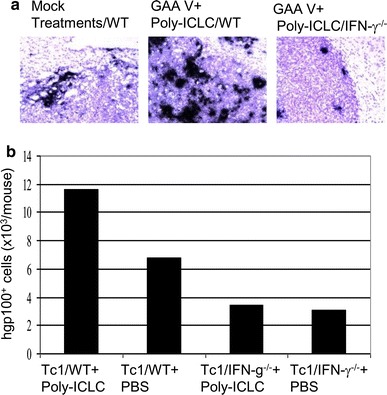
Poly-ICLC promotes the infiltration of effector T cells into intracranial gliomas via induction of CXCL10 in IFN-α and IFN-γ dependent manners | SpringerLink

JCI - Intranasal Poly-IC treatment exacerbates tuberculosis in mice through the pulmonary recruitment of a pathogen-permissive monocyte/macrophage population

Poly-IC enhances the effectiveness of cancer immunotherapy by promoting T cell tumor infiltration | Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer
Synthetic Double-Stranded RNAs Are Adjuvants for the Induction of T Helper 1 and Humoral Immune Responses to Human Papillomavirus in Rhesus Macaques | PLOS Pathogens

JCI - Intranasal Poly-IC treatment exacerbates tuberculosis in mice through the pulmonary recruitment of a pathogen-permissive monocyte/macrophage population

Enhancing the immune stimulatory effects of cetuximab therapy through TLR3 signalling in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) positive nasopharyngeal carcinoma. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Role of MDA5 and interferon-I in dendritic cells for T cell expansion by anti-tumor peptide vaccines in mice. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Poly‐ICLC preconditioning protects the blood–brain barrier against ischemic injury in vitro through type I interferon signaling - Gesuete - 2012 - Journal of Neurochemistry - Wiley Online Library